The hemp plant produces over a hundred different cannabinoids, but researchers have only just scratched the surface of their potential benefits. Some of these cannabinoids, such as CBD, THC, and CBN, are more familiar. Recently, there has been significant media attention on the “varin” family of molecules, including cannabivarin (CBDV) and tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV). THCV has been dubbed “diet weed” due to claims that it might aid in weight loss.
In this post, we’ll discuss:
- What THCV is
- How it’s different from THC
- THCV’s potential benefits
What is THCV?
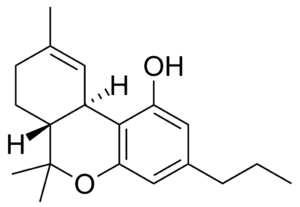
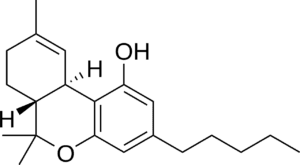
Tetrahydrocannabivarin, is one of over a hundred different cannabinoids produced by the hemp plant. Is the activated, or decarboxylated, form of tetrahydrocannabivarin acid (THCVa) and is non-intoxicating. It acts as a dose-dependent CB1 agonist and antagonist and a CB2 agonist. Also interacts with various transient receptor potential (TRP) channels as both an agonist and antagonist. This complex interaction suggests many potential uses.
To understand the significance of THCV, it’s important to delve deeper into its chemical structure and how it interacts with our body. The decarboxylation process, which converts THCVa to THCV, is crucial. Decarboxylation involves the removal of a carboxyl group from the cannabinoid acid, which occurs when the plant material is exposed to heat or light. This process activates the cannabinoid, allowing it to interact with the endocannabinoid system in our bodies.
Where Can I Find THCV?
It is not found in high concentrations in most commercially available hemp. However, some hemp cultivars have been bred to produce high concentrations of THCV. Leafly, a cannabis media website, reports that certain African Landrace Sativa cultivars produce substantial amounts of THCV. Can also be isolated from hemp and cannabis in a laboratory and concentrated for use in manufactured products.
These specialized cultivars have been developed through selective breeding techniques. By choosing plants that naturally produce higher levels of THCV, breeders have been able to enhance this trait over several generations. The result is hemp varieties that are specifically grown for their THCV content. This process of selective breeding is not new and has been used for centuries to develop plants with desirable characteristics, such as higher yields or better resistance to pests.
The extraction process to isolate THCV involves several steps. Initially, the plant material is harvested and dried. The dried material is then processed to separate the cannabinoids from the plant fibers. This is typically done using a solvent, such as ethanol or CO2, which dissolves the cannabinoids. The solvent is then evaporated, leaving behind a concentrated extract that contains THCV and other cannabinoids. Further purification steps are needed to isolate THCV from the other compounds in the extract.
THCV vs. THC: What’s the Difference?
Despite their similar names and chemical compositions, THCV and THC behave quite differently. THC is well-known for its psychoactive effects, which result from activating the CB1 receptors in the brain, producing a “high.” In contrast, THCV is non-intoxicating and does not produce a “high.” THCV can block the CB1 receptor and has been shown to counteract some of THC’s effects in research using mice.
Understanding the differences between THCV and THC requires a closer look at their molecular structures. THC and THCV share a similar backbone, but THCV has a three-carbon side chain instead of the five-carbon side chain found in THC. This small difference in structure results in significant differences in their effects on the body.
The interaction with the endocannabinoid system is also unique. As a dose-dependent CB1 agonist and antagonist, THCV can either stimulate or inhibit the CB1 receptor depending on the dose. This means that at low doses, THCV may act as an antagonist, blocking the receptor and preventing activation by other cannabinoids. At higher doses, it may act as an agonist, stimulating the receptor and producing effects similar to other cannabinoids.
What Are Researchers Finding?
Research into possible benefits is still in its infancy, but interest is growing. Here are some findings from various studies:
- In a double-blind 2016 pilot study, THCV combined with CBD showed potential therapeutic benefits for patients with type-2 diabetes.
- In small doses, THCV may prevent some effects of Delta-9 THC, such as THC-induced hypothermia.
Other potential effects being researched include:
- Weight loss/decrease in body fat
- Appetite suppression/regulation
- Anticonvulsant properties
- Hyperalgesia suppression
- Anti-inflammatory effects
- Acne treatment
- Anti-addiction effects
- Antiemetic properties
Most of this research has been conducted either in vitro or in animal models, so we must wait to see what the implications are for humans. However, the research has been promising, and it appears we will be hearing more in the coming years.
The potential weight loss effects of THCV have garnered considerable attention. Has been shown to suppress appetite and increase energy expenditure in animal studies. These effects could make THCV a valuable tool in the fight against obesity and related metabolic disorders. The exact mechanisms by which THCV exerts these effects are not yet fully understood, but it is believed to involve modulation of the endocannabinoid system and other metabolic pathways.
In addition to its potential metabolic benefits, THCV has shown promise as an anticonvulsant. Studies have demonstrated that THCV can reduce seizure activity in animal models of epilepsy. This effect is thought to be mediated through its interaction with TRP channels and the endocannabinoid system. If these findings can be replicated in human studies, THCV could become a new treatment option for patients with epilepsy and other seizure disorders.
The anti-inflammatory effects are another area of active research. Inflammation is a common underlying factor in many chronic diseases, including arthritis, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative disorders. By reducing inflammation, THCV may help to alleviate symptoms and slow the progression of these conditions. Preliminary studies have shown that THCV can inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and reduce inflammation in animal models.
THCV’s potential to treat acne is also being explored. Acne is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by the overproduction of sebum, an oily substance that can clog pores and lead to inflammation. THCV has been shown to reduce sebum production and inhibit the growth of acne-causing bacteria in laboratory studies. If these effects can be confirmed in clinical trials, THCV could become a new option for acne treatment.
The anti-addiction effects of THCV are particularly intriguing. Addiction is a complex condition that involves changes in the brain’s reward system. THCV has been shown to reduce the rewarding effects of addictive substances, such as nicotine and cocaine, in animal studies. This suggests that THCV could be used as a treatment for addiction, helping individuals to overcome their dependence on harmful substances.
Lastly, antiemetic properties are being studied for their potential to treat nausea and vomiting. These symptoms are common side effects of chemotherapy and other medical treatments. Preliminary studies have shown that THCV can reduce nausea and vomiting in animal models, suggesting that it could be a useful adjunct therapy for patients undergoing chemotherapy. Visit Sunset Lake CBD.
FAQs
What is?
- THCV, or tetrahydrocannabivarin, is a non-intoxicating cannabinoid found in the hemp plant that may have various potential health benefits.
How does THCV differ from THC?
- While THC is known for its psychoactive effects, THCV does not produce a “high” and can actually block some of THC’s effects.
Where can I find THCV?
- Can be found in certain hemp cultivars, particularly some African Landrace Sativa strains. It can also be isolated and concentrated in a laboratory.
What are the potential benefits ?
- Potential benefits of THCV include weight loss, appetite suppression, anticonvulsant properties, anti-inflammatory effects, and more.
Is legal?
- The legality varies by region and is often dependent on the source of the THCV (hemp or cannabis) and local regulations.