No products in the cart.
What Is Cannabidiol?
Cannabidiol, commonly known as CBD, is finding its way into just about every wellness product these days. You may have seen it touted for its relaxation and sleep benefits, but are such claims warranted? In this post, we’ll explore what cannabidiol is, how it works with your body’s native endocannabinoid system, and how you can use it safely.
Key Takeaways: What Is Cannabidiol?
- Cannabidiol, the formal name of CBD, is a cannabinoid produced by mature hemp and cannabis plants.
- Cannabidiol facilitates the uptake of beneficial endogenous cannabinoids that our bodies make, allowing our ECS to work more effectively.
- CBD use is generally considered safe, but you should check with a health professional before adding it to your daily routine.
Table of contents:
What Is Cannabidiol (CBD)?
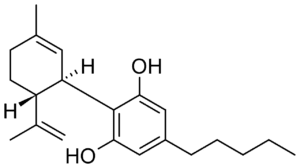
Cannabidiol (CBD) is one of the 100+ naturally occurring cannabinoids produced by mature hemp plants. Cannabis (also known as marijuana) plants also produce CBD, though in smaller concentrations.
Unlike its molecular cousin, THC, CBD doesn’t make users feel intoxicated in any way. According to a 2017 memo from the World Health Organization, cannabidiol exhibits “…no effects indicative of any abuse or dependence potential…” meaning that you can’t abuse or become addicted to it.
A more recent study in Neuropsychopharmacology concluded that “…CBD alone is unlikely to significantly impair daily functioning or workplace performance.”
How is cannabidiol different from THC?
Both CBD and THC are cannabinoids produced by hemp and cannabis plants, but their similarities generally end there. Cannabidiol is non-psychoactive and used for its wellness benefits, which we’ll explore a little later.
THC, on the other hand, is often used for its psychoactive and intoxicating effects.
How does cannabidiol work?
Cannabidiol works with our body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS), which is a system that all mammals share. In simple terms, the ECS is a network of receptors located all over our bodies that help with vital functions like,
- Sleep quality and quantity
- Mood and emotional regulation
- Stress and response
- Appetite and metabolism
- Memory and learning
- Inflammation and immune response
When consumed, other cannabinoids usually interact with our ECS receptors and cause different effects. CBD works differently. Instead of binding with ECS receptors, CBD helps the whole system run more efficiently.
Cannabidiol and our endocannabinoid system
Here are a few key ways that we believe cannabidiol helps your endocannabinoid system work more efficiently.
- Modulating receptor activity – Unlike THC, CBD doesn’t bind directly to our ECS’s CB receptors but is believed to facilitate or prevent the uptake of specific endocannabinoids. For example, CBD can help prevent the uptake of adenosine, an endocannabinoid that your body uses to stay awake.
- Interacting with non-ECS receptors – CBD also interacts with other receptors in the body. For instance, it can activate serotonin receptors, which play a role in mood regulation and anxiety. This interaction might explain why some users find that CBD can alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression.
- Reducing inflammation – CBD has anti-inflammatory properties, making it beneficial for conditions involving inflammation, such as arthritis and multiple sclerosis.1 By reducing inflammation, CBD may be able to alleviate pain and improve overall health.
Cannabidiol health benefits
CBD has been touted as a treatment for a variety of health conditions and ailments. We preface this section by stating that in no way is cannabidiol a panacea, but there are some well-documented benefits of its use.
Some FDA studies, animal studies, and self-reported research in humans suggest that cannabidiol may help with:
- Seizure management – Of all the potential benefits of CBD, seizure management is the most documented. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved cannabidiol-derived Epidiolex to treat the rare seizure disorders Dravet syndrome and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome.
- Pain relief – Many people use CBD for its pain-relieving properties. It may help manage chronic pain by influencing endocannabinoid receptor activity, reducing inflammation, and interacting with neurotransmitters. One animal study from the European Journal of Pain suggests that CBD may help lower pain caused by arthritis when applied topically.5
- Heart health – CBD’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties may contribute to improved heart health. Some studies have shown that CBD can lower high blood pressure, a significant risk factor for heart disease.2
- Addiction – According to self-reported research in humans, CBD may lower cravings for tobacco and opioids under the right conditions. Animal studies suggest that it may also help reduce cravings for other addictive substances like alcohol and stimulants.6
- Anxiety – CBD has shown promise in treating anxiety, likely through its ability to interact with serotonin receptors.3 This makes it a natural alternative to pharmaceutical drugs, which can have adverse side effects.

How to consume cannabidiol
You can consume cannabidiol in any number of ways. We’ll explore some of the most common in this section. But first, let’s note that as CBD technology improves, we expect to see new and more exciting methods coming out in the next few years.
Sublingual
Sublingual means under the tongue. Many people who use CBD oil or CBD tinctures will opt to use them under their tongue. The membrane under your tongue is thin and allows for quicker absorption of CBD into your bloodstream.
Ingestion
Ingestion covers most CBD edibles and beverages. When you consume or ingest CBD, it has to reach your stomach and intestines before it reaches your bloodstream. Generally, though, when you ingest cannabidiol, the beneficial effects will last longer.
Inhalation
When you smoke or inhale hemp, the cannabidiol inside will reach peak concentration in your bloodstream in three minutes.4 Many users who opt for inhalation tend to do so because of how rapidly they find relief.
Topically
You can also use topical CBD for localized benefits. Your skin, just like every other organ in your body, contains ECS receptors and can benefit from CBD.
Frequently asked questions about cannabidiol
Difference between cannabidiol vs. CBD
Though we understand the confusion, there is no discernable difference between cannabidiol and CBD. CBD is the shortened version of the word canna-bi-diol (emphasis is ours).
Is CBD legal?
CBD, the cannabinoid itself, is legal and readily available in the United States thanks to the 2018 Farm Bill. Some states have instituted their own hemp and CBD rules, but they don’t affect the national market in any meaningful way.
Is hemp cannabidiol?
Hemp, the plant and agricultural product, is not cannabidiol. However, we do derive cannabidiol from the hemp plant. More specifically, we extract cannabidiol from mature hemp flowers.
Is cannabidiol safe?
Cannabidiol is generally considered safe. Some side effects of CBD use include,
- Nausea
- Fatigue
- Irritability
- Upset stomach
- Blood thinning
If you’re on any blood-thinning or anti-epileptic medications, you should consult your doctor or pharmacist before you add CBD to your supplement regimen.
Sources
- Atalay, Sinemyiz et al. “Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Cannabidiol.” Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 9,1 21. 25 Dec. 2019, doi:10.3390/antiox9010021
- Jadoon, Khalid A et al. “A single dose of cannabidiol reduces blood pressure in healthy volunteers in a randomized crossover study.” JCI insight vol. 2,12 e93760. 15 Jun. 2017, doi:10.1172/jci.insight.93760
- De Gregorio, Danilo et al. “Cannabidiol modulates serotonergic transmission and reverses both allodynia and anxiety-like behavior in a model of neuropathic pain.” Pain vol. 160,1 (2019): 136-150. doi:10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001386
- Millar, Sophie A et al. “A Systematic Review on the Pharmacokinetics of Cannabidiol in Humans.” Frontiers in pharmacology vol. 9 1365. 26 Nov. 2018, doi:10.3389/fphar.2018.01365
- Hammell, D C et al. “Transdermal cannabidiol reduces inflammation and pain-related behaviours in a rat model of arthritis.” European journal of pain (London, England) vol. 20,6 (2016): 936-48. doi:10.1002/ejp.818
- Prud’homme, Mélissa et al. “Cannabidiol as an Intervention for Addictive Behaviors: A Systematic Review of the Evidence.” Substance abuse : research and treatment vol. 9 33-8. 21 May. 2015, doi:10.4137/SART.S25081
Photos courtesy of Wikimedia user Cacycle