What Is CBDV & What Is It Used For?
It seems like almost every month we are now hearing about a new and exciting cannabinoid. You’ve probably heard of THC and CBD. But what about CBDV? CBDV, short for cannabidivarin, is getting some media attention lately. And, while hemp research has been hindered for decades by international prohibition, thankfully there are intrepid scientists who wade through rivers of restrictive governmental red tape in order to conduct groundbreaking cannabinoid research.
In this post, we’ll explore,
- What CBDV is
- How it’s different than CBD
- What the research says about its applications
What Is CBDV?
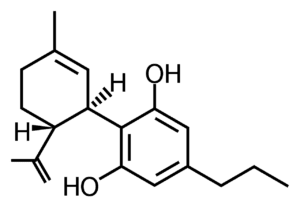
Here’s where we get a little technical. Cannabidivarin (CBDV) is one of over one hundred phytocannabinoids found in cannabis. Although it is not typically found in high concentrations, some cultivars, such as Forbidden V and Pine Walker, have been bred to express substantial quantities of CBDV.
CBDV is the decarboxylated, or activated form of, cannabidivarinic acid (CBDVA). Technicians first isolated this non-intoxicating molecule in 1969 and has a weak affinity for both CB1 and CB2 receptors1. CBDV is the chemical precursor to THCV.
CBDV Vs. CBD: What’s The Difference?
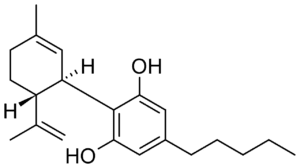
The differences between CBDV vs. CBD start at the molecular level. Whereas CBD has a pentyl (5) chain of carbons, CBDV only has a propyl (3) chain. CBDV is just like CBD in every other way— it just has a shorter carbon tail!
That’s not where the differences end though. CBDV has also been observed interacting with transient receptor potential TRP channels. TRP channels are involved in2:
- Production of inflammatory mediators
- Phagocytosis
- Cell migration
What Are Researchers Finding— Potential CBDV Benefits
Researchers have taken note of CBDV as a potentially useful cannabinoid for various therapeutic applications owing to the fact that it doesn’t produce intoxicating effects.
Here is a list of research regarding CBDV:
- GW Pharmaceuticals is planning a phase 2 clinical trial of a CBDV-containing drug to treat epilepsy in adults1,10.
- Drugs containing CBDV are being researched for the treatment of children and adults with Autism Spectrum Disorder3,4.
- “Chronic treatment with the phytocannabinoid Cannabidivarin (CBDV) rescues behavioural alterations and brain atrophy in a mouse model of Rett syndrome5”
- Research with rats indicates CBDV may be useful for reducing nausea6.
- Study of non-intoxicating phytocannabinoids, including CBDV, using mice modeling Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD)7.
- A phase 2 clinical trial is underway to explore whether cannabis oil containing CBDV (and other cannabinoids) could be helpful for adults with ADHD8.
- A 2016 study suggested that CBDV might provide relief from acne1,9.
Where Can You Buy CBDV?
Good news! Sunset Lake CBD grows some cultivars that contain CBDV including Forbidden V. Forbidden V was bred by Oregon CBD and grown under the sun on our farm in South Hero, Vermont. With 6.85% CBDV and 11.94% CBD, the buds hold a lot of promise for a variety of uses.
You can use Forbidden V on its own (smoked or vaped) or extract CBDV from the plant material to make oil tinctures, topicals, and edibles.
Currently, Forbidden V is only available to wholesale customers. If you’re a retailer interested in carrying Forbidden V, please get in touch with us here.
Sources:
- Ahmad, S., & Hill, K. P. (2021). Medical marijuana: A clinical handbook. Wolters Kluwer. pp. 105 & 373.
- Pretzsch, C.M., Voinescu, B., Lythgoe, D. et al. Effects of cannabidivarin (CBDV) on brain excitation and inhibition systems in adults with and without Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): a single dose trial during magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Transl Psychiatry 9, 313 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-019-0654-8
- Pretzsch, C.M., Voinescu, B., Lythgoe, D. et al. Effects of cannabidivarin (CBDV) on brain excitation and inhibition systems in adults with and without Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): a single dose trial during magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Transl Psychiatry 9, 313 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-019-0654-8
- Cannabidivarin (CBDV) vs. Placebo in Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03202303
- Chronic treatment with the phytocannabinoid Cannabidivarin (CBDV) rescues behavioural alterations and brain atrophy in a mouse model of Rett syndrome. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30056123/
- Rock, E. M., Sticht, M. A., Duncan, M., Stott, C., & Parker, L. A. (2013). Evaluation of the potential of the phytocannabinoids, cannabidivarin (CBDV) and Δ(9) -tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV), to produce CB1 receptor inverse agonism symptoms of nausea in rats. British journal of pharmacology, 170(3), 671–678. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.12322
- Iannotti, F. A., Pagano, E., Moriello, A. S., Alvino, F. G., Sorrentino, N. C., D’Orsi, L., Gazzerro, E., Capasso, R., De Leonibus, E., De Petrocellis, L., and Di Marzo, V. (2019) Effects of non-euphoric plant cannabinoids on muscle quality and performance of dystrophic mdx mice. British Journal of Pharmacology, 176: 1568– 1584. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.14460.
- Treatment With Cannabis Oil Containing CBD, THC, CBDV or CBG vs. Placebo of Persons With ADHD. https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05219370
- Oláh, Attila & Markovics, Arnold & Szabó-Papp, Judit & Szabó, Pálma & Stott, Colin & Zouboulis, Christos & Bíró, Tamás. (2016). Differential effectiveness of selected non-psychotropic phytocannabinoids on human sebocyte functions implicates their introduction in dry/seborrheic skin and acne treatment. Experimental dermatology. 25. 10.1111/exd.13042.
- Havelka, J. (2021). What is CBDV (cannabidivarin) & what does this cannabinoid do? Leafly. https://www.leafly.com/news/cbd/what-is-cbdv-cannabidivarin-marijuana-cannabinoid