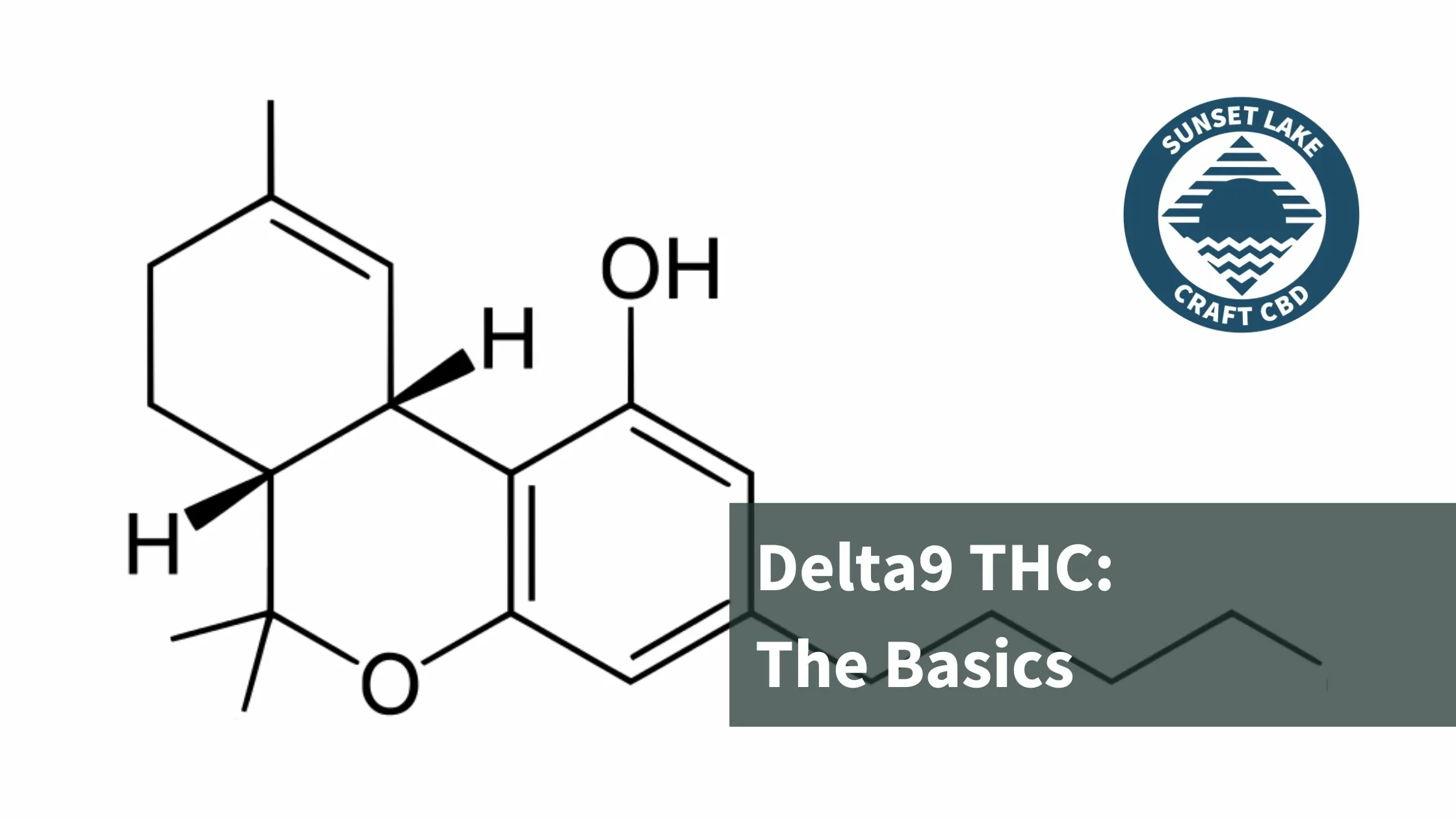
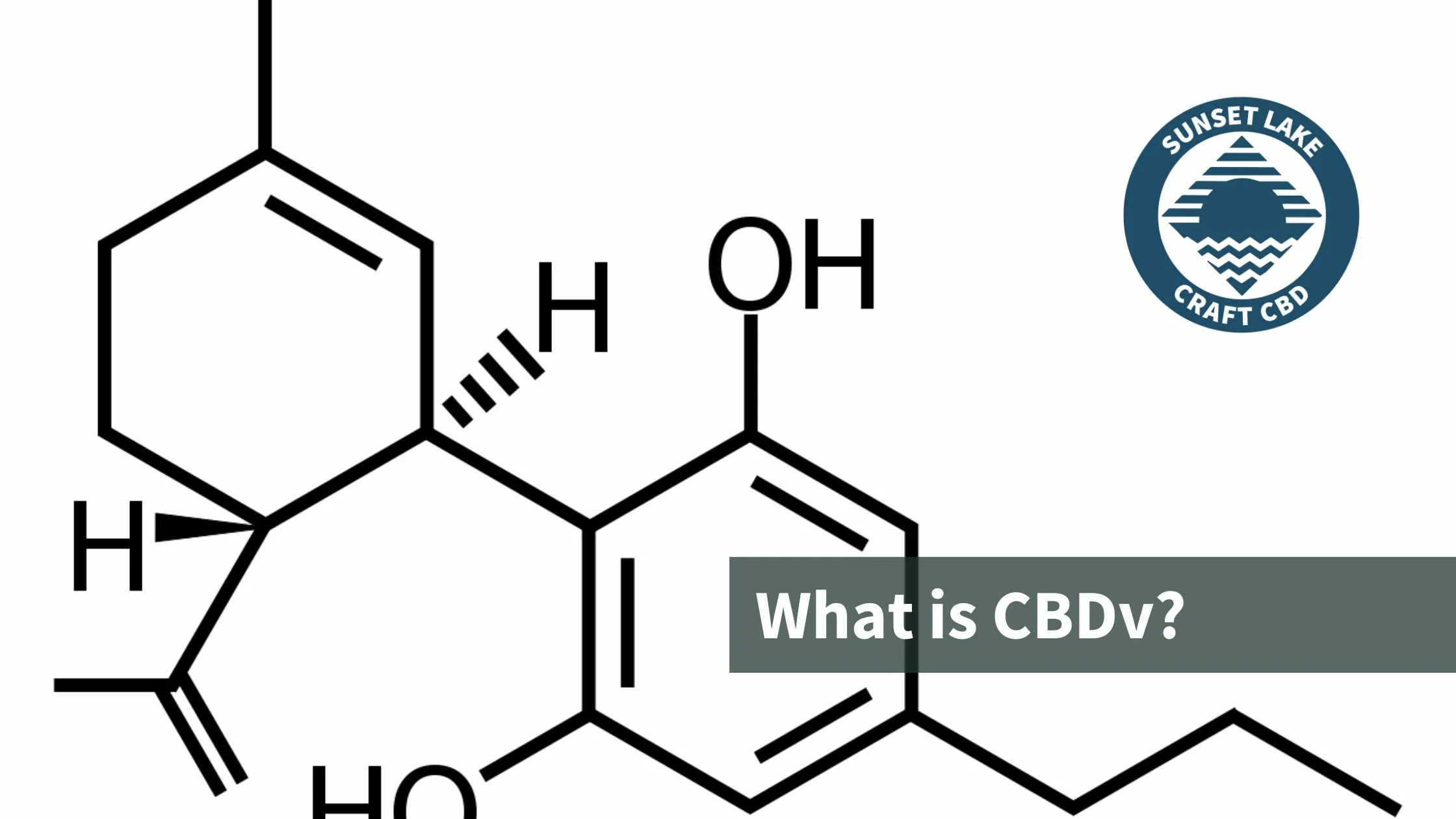
As CBD’s therapeutic effects grow in popularity, other parts of the hemp plant beyond cannabinoids are also gaining attention. Terpenes are a class of organic chemicals that cannabis and hemp flower cultivators and manufacturers are beginning to highlight.
In this post, we’ll answer several questions about terpenes, including:
- What are terpenes?
- What are they made of?
- What are the benefits of terpenes?
- What’s so special about hemp flower terpenes?
What Are Terpenes?
Terpenes are molecules responsible for the aroma of fruits, flowers, and even some animals. For example, limonene gives citrus fruits their characteristic acidic, clean-smelling aroma. In technical terms, they are volatile aromatic hydrocarbons, which means they evaporate at room temperature, allowing us to smell and taste them.
Terpenes play a significant role in the plant kingdom. They are involved in the aroma and the plant’s defense mechanisms. Many plants produce terpenes to ward off herbivores and attract pollinators. This dual role highlights the importance of terpenes in the natural world.
What Are Terpenes Made Of?
Terpenes are simple organic molecules composed of building blocks called isoprenes. Isoprenes contain five carbon atoms and eight hydrogen atoms. We classify terpenes based on the number of isoprene units they contain.
- Monoterpenes: Two isoprene units.
- Sesquiterpenes: Three isoprene units.
- Diterpenes: Four isoprene units.
Each type of terpene has unique properties and can be found in various plants. For instance, monoterpenes are often found in essential oils and are known for their strong aromas.
Sesquiterpenes tend to be more stable and are found in spices and medicinal plants. Diterpenes are larger molecules and are often found in resins and certain types of trees.
How Are Terpenes Different from CBD?
Terpenes and cannabinoids, like CBD, are different types of molecules that serve distinct functions. While cannabinoids interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system, terpenes generally do not. Cannabinoids are primarily found in cannabis and hemp plants, whereas terpenes can be found in most plants, consumer products, cosmetics, cleaning agents, and fruits. However, cannabis and hemp flower terpenes and cannabinoids can work together to create different effects on users.
The interaction between terpenes and cannabinoids is often referred to as the “entourage effect.” This concept suggests that the combined effects of cannabinoids and cannabis terpenes can enhance the overall therapeutic benefits. For example, the calming effects of CBD might be amplified by the presence of linalool, a terpene known for its relaxing properties.
Why Do They Matter?
Terpenes provide the aroma and flavor of hemp and cannabis. They may also offer several benefits, although research is still ongoing. Some well-known terpenes and their potential effects include:
Β-Myrcene
Found in mangoes, thyme, lemongrass, and hops, myrcene may help with:
- Managing inflammation2
- Pain relief2
- Sedation, especially when mixed with CBD and THC2
- Muscle relaxation3
- Anti-osteoarthritic effects3
- Neuroprotection3
Myrcene is one of the most abundant terpenes in cannabis. Its presence can significantly influence the overall effects of a particular strain. For instance, cultivars that are high in myrcene are often associated with relaxing and sedative effects, making them popular choices for evening use.
Β-Caryophyllene
Present in black peppercorns, cloves, cinnamon, hops, and rosemary, caryophyllene may assist with:
- Managing inflammation3
- Protecting the gastric system from harmful substances2
- Blocking pain3
Caryophyllene is unique among terpenes because it can interact directly with the body’s endocannabinoid system, specifically the CB2 receptors. This interaction makes it particularly effective in managing inflammation and pain, offering potential therapeutic benefits that are still being explored in scientific research.

Limonene
Common in juniper berries, citrus fruits, and some conifer trees, limonene may have:
- Immunostimulation²
- Anxiolytic² (anti-anxiety effects)
- Antibacterial²
Limonene is not only valued for its uplifting citrus aroma but also for its potential health benefits. Studies have shown that limonene can enhance mood and alleviate stress, making it a popular choice in aromatherapy. Additionally, its antibacterial properties make it a valuable component in natural cleaning products and cosmetics.
Terpinolene
Found in lilacs, nutmeg, cumin, apples, and tea trees, terpinolene may offer:
- Antioxidant effects³
- Sedative effects³
Terpinolene is less common than other terpenes but still plays a crucial role in the overall profile of certain cannabis strains. It is known for its fresh, herbal aroma and is believed to contribute to the sedative effects of certain strains, making it beneficial for promoting relaxation and sleep.
Pinene
Most prevalent in pine trees, pinene may provide:
- Antibiotic effects
- Bronchodilation
- Memory aid
Pinene is one of the most common terpenes in nature, found in pine trees, rosemary, and basil. It is known for its potential to improve airflow and respiratory function, which can be particularly beneficial for individuals with asthma. Additionally, pinene has been studied for its ability to enhance memory and cognitive function.
Linalool
Present in lavender, rose, and mint, linalool is believed to:
- Act as a sedative
- Help treat burns
- Serve as an anticonvulsant
- Act as a local anesthetic
Linalool is widely recognized for its calming and relaxing effects, making it a popular ingredient in aromatherapy and personal care products. Its ability to act as a sedative and local anesthetic makes it valuable in medical applications, particularly for managing anxiety and pain.
Ocimene
Found in basil, parsley, mint, kumquats, and hemp, ocimene may have:
- Anti-fungal properties
- Anti-inflammatory effects
- Anti-viral properties
Ocimene is known for its sweet, floral aroma and is commonly used in perfumes and fragrances. Its potential antifungal and anti-inflammatory properties make it an attractive candidate for therapeutic use, particularly in managing respiratory conditions and infections.
Bisabolol
Found in sage and the candela tree, bisabolol may provide:
- Anti-inflammatory effects
- Gastroprotective effects
- Pain relief
Bisabolol is commonly found in chamomile and is known for its soothing and calming effects. It is often used in skincare products for its anti-inflammatory and healing properties, making it beneficial for treating skin conditions such as eczema and dermatitis.
Humulene
Humulene is often associated with the characteristic aroma of hops, a key ingredient in beer. It has been studied for its potential to suppress appetite and reduce inflammation, making it a valuable component in weight management and anti-inflammatory treatments.
How Do Terpenes Make You Feel?
Terpenes can modulate user experience, contributing to the entourage effect. Their specific effects can vary depending on their concentration and combination with other cannabinoids like THC and CBD.
For instance, a strain high in myrcene and linalool might produce a relaxing, sedative effect, while a strain high in limonene and pinene might result in a more uplifting and energizing experience. Understanding the terpene profile of a particular strain can help users select the right product for their desired effects.
What Are The Benefits Of Terpenes?
It’s difficult to definitively say if terpenes are good for you based on current studies. We do know that they are generally safe to consume, as we find them in fruits, herbs, and spices. The potential therapeutic benefits of terpenes are still being researched, but early studies suggest that they may offer a range of health benefits.
For example, terpenes like limonene and linalool are often used in aromatherapy for their mood-enhancing and stress-relieving properties. Other terpenes, such as pinene and caryophyllene, are being studied for their potential to treat respiratory conditions and inflammation. While more research is needed, the existing evidence points to the potential for terpenes to play a significant role in natural health and wellness.
How Sunset Lake CBD Cultivars Compare
Our hemp cultivars contain a wide range of terpenes. Below are our current cultivars and their top three terpenes:
- Lifter: Myrcene, β-caryophyllene, α-pinene, humulene
- Sour Lifter: Terpinolene, β-caryophyllene, myrcene, humulene
- Hawaiian Haze: Myrcene, α-pinene, β-caryophyllene, β-pinene
- Sour Hawaiian Haze: Myrcene, terpinolene, α-pinene, β-caryophyllene
- Suver Haze: Myrcene, β-caryophyllene, α-pinene, humulene
- Sour Suver Haze: Myrcene, terpinolene, β-caryophyllene, humulene
- Special Sauce: Myrcene, β-caryophyllene, α-pinene, limonene
- Super Sour Space Candy: Terpinolene, myrcene, β-caryophyllene, humulene
- Cherry Abacus: Myrcene, α-pinene, β-caryophyllene, β-pinene
Conclusion
Understanding their effects can enhance your appreciation of hemp and cannabis products. By exploring the unique properties of each terpene, you can better tailor your experience to meet your specific needs. As research continues to uncover the potential benefits of terpenes, we look forward to learning more about their role in natural health and wellness. Visit Sunset Lake CBD.
FAQs
- What are terpenes?
- It is an aromatic molecule found in many plants and some animals, responsible for their distinct scents.
- How do terpenes differ from cannabinoids like CBD?
- Terpenes and cannabinoids are different types of molecules; cannabinoids interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system, while terpenes contribute to aroma and may have various effects.
- Can terpenes affect how I feel?
- Yes, terpenes can modulate the user experience and contribute to the entourage effect, which affects whether users feel energized or relaxed.
- Are terpenes safe to use?
- It is are generally considered safe as they are found in many common products like fruits, cosmetics, and scented candles.
- Do all hemp cultivars contain the same terpenes?
- No, different hemp cultivars contain varying types and concentrations of terpenes, which can affect their aroma and potential effects.
Sources:
- Ben-Shabat, S., Fride, E., Sheskin, T., Tamiri, T., Rhee, M. H., Vogel, Z., Bisogno, T., De Petrocellis, L., Di Marzo, V., & Mechoulam, R. (1998). An entourage effect: inactive endogenous fatty acid glycerol esters enhance 2-arachidonoyl-glycerol cannabinoid activity. European journal of pharmacology, 353(1), 23–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-2999(98)00392-6
- Russo E. B. (2011). Taming THC: potential cannabis synergy and phytocannabinoid-terpenoid entourage effects. British journal of pharmacology, 163(7), 1344–1364. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01238.x
- Ahmad, Samoon, and Kevin P. Hill. “The Pharmacodynamics of Cannabis.” Medical Marijuana: A Clinical Handbook, Wolters Kluwer, Philadelphia, 2021, pp. 264–286.
- Fernandes, E. S., Passos, G. F., Medeiros, R., da Cunha, F. M., Ferreira, J., Campos, M. M., Pianowski, L. F., & Calixto, J. B. (2007). Anti-inflammatory effects of compounds alpha-humulene and (-)-trans-caryophyllene isolated from the essential oil of Cordia verbenacea. European journal of pharmacology, 569(3), 228–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.04.059
Updated:
May 25, 2024